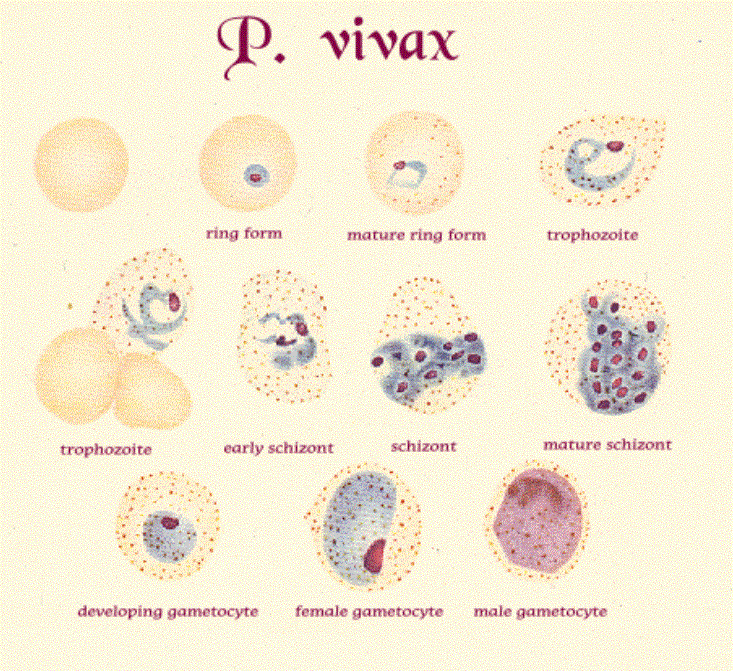
MALARIA ×ÜðçÚØæ
Cause: Transmitted
by the female anopheline mosquito when she drinks human blood (males
feed on plant juices). The disease is
caused by several species of protists (i.e. protozoans), and there is much
geographic variability.
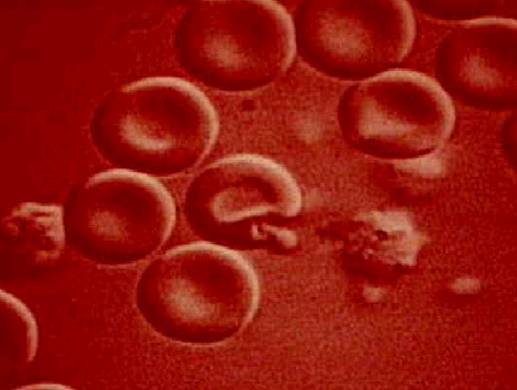
Malaria
(parasite) Red Blood 

![]()
Cells![]()
Symptoms: Fever,
shivering, pain in the joints and headache.
It takes 8 to 4 weeks incubation.
300 million affected worldwide;
1 to 1.5 million die per year.
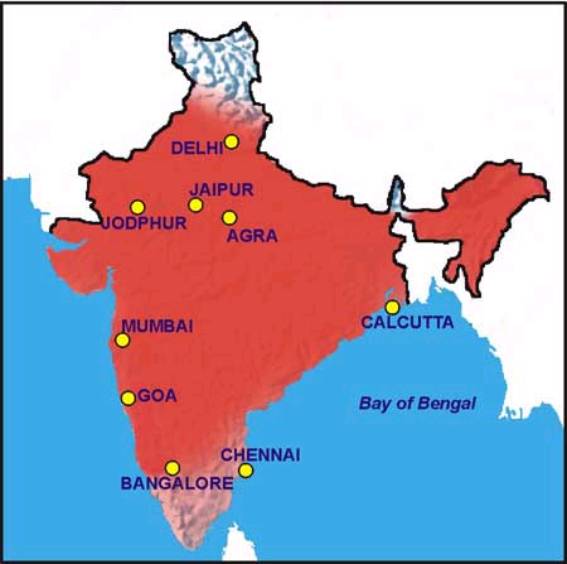
About 2 million infections/year in India. Malaria is not common in Jammu, but the highest risk is during summer, immediately after the monsoon.
DENGUE Çð‹»ê
ÈèßÚ
Cause: An
RNA virus spread by the aegypti mosquitoe (different from anopheline of
malaria). There are fours sub-types of
Dengue; DEN-1,2,3,4, and they are do not-cross immunify.
Symptoms: Hemorraghing, viral illness
MOSQUITOES ×ÊÀÚ

Human ![]()
Skin


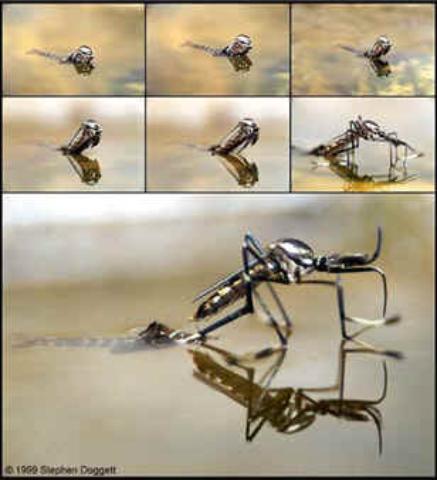
Eggs Water![]()

Mosquitoes of lay 100 to
400 eggs in “egg rafts” that float in still or stagnant water. The larvae feed on micro-organisms before
maturing.

ANAEMIA ÚQ ãèÙÌæ
Cause:
Anaemia is the general weakening of the blood due to improper diet, esp. a lack
of iron.
Symptoms: Fatigue,
weakness
Treatment: Iron is a critical component of hemoglobin in red blood
cells since it binds to oxygen.
You need to eat green vegetables to get your iron
intake, as well as Vit’s B1, B6, and B12.

TYPHOID Å槚
æò§Ç …ßÚ
Cause: Food or drink water that has been infected with Salmonella typhi. (17 million cases, and 600,000 deaths/year.)
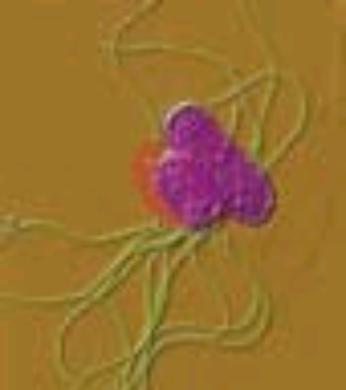
Symptoms: The sudden onset of sustained fever, severe headache, nausea and
severe loss of appetite. It is sometimes accompanied by hoarse cough and
constipation or diarrhoea.
Treatment: Case-fatality rates of 10% can be reduced to less than 1%
with appropriate antibiotic therapy.
NALIS ÙæÜè

DYSENTERY
Âðç¿K
Cause: Shigella dysenteriae bacteria or Entamoeba
histolytica amoeba
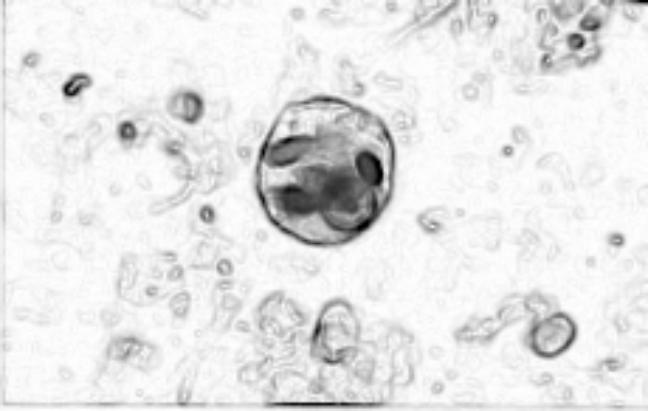
Symptoms: severe,
often bloody diarrhea, vomitting, fever.
Treatment: Several drugs available... life-threatening if untreated Approximately 5-15% of Sd1 cases are fatal.
WORMS ·ê
ç×
Cause: Parasites enter either through food or
through feet. Affects around 1 billion
people.
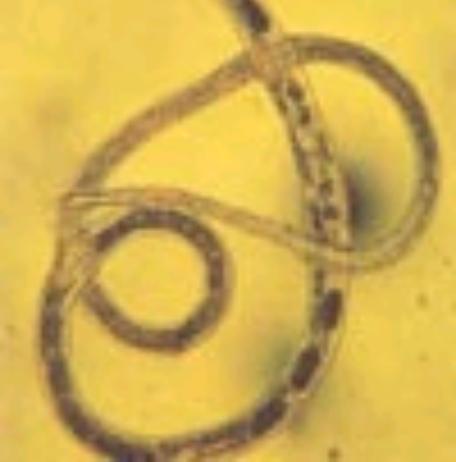
Symptoms: Variety
of symptoms
Treatment: Several drugs like Albendazole can remove worms.
CHOLERA ãñœæ
Cause: Vibrio cholerae bacteria
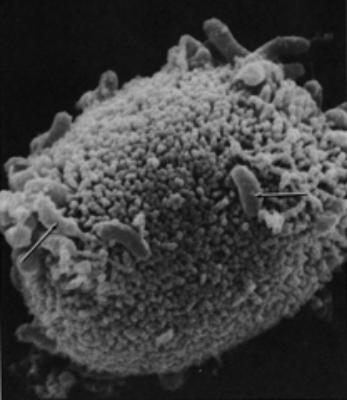
Symptoms: causes diarrhea, dehydration. When illness does occur, more than 90% of episodes are
mild. Less than 10% of ill persons develop typical cholera with signs of
moderate or severe dehydration
Treatment: Several drugs available... life-threatening if untreated
HIV/AIDS °Ç÷#
Cause: Deadly virus transmitted through blood.
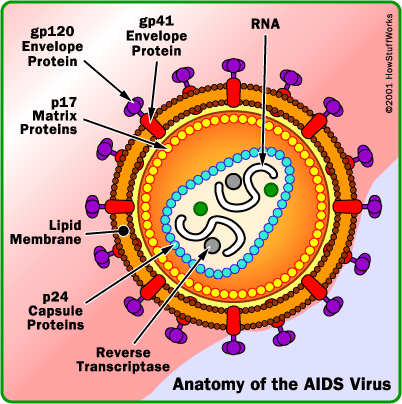
Symptoms: General weakness of body and suspceptibility to
illness.
Treatment: No treatment currently exsists. Most infected patients die within 5 to 10
years of infection. There are some
“cocktail” drugs that can slow the progression of the disease.
MALARIA ×ÜðçÚØæ
Malaria (parasite)